IMPETIGO
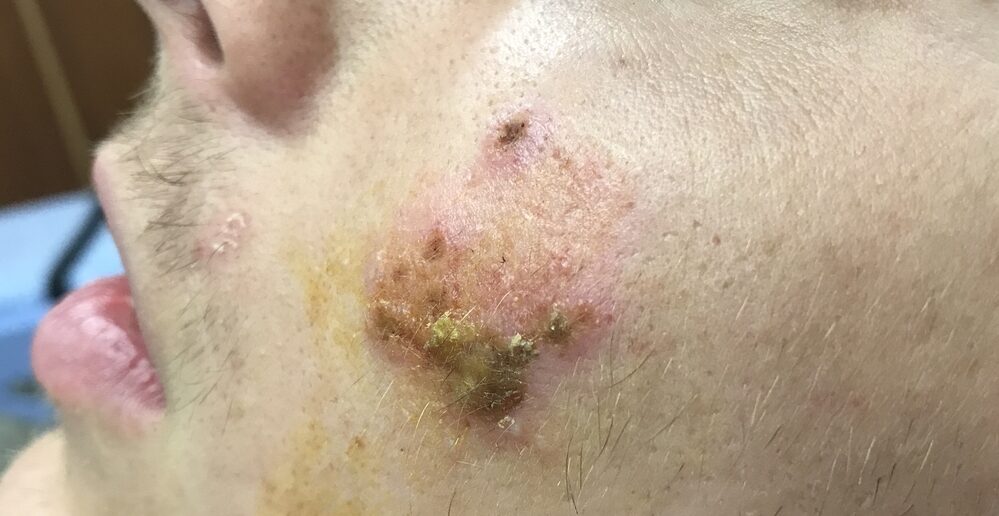
Causes, Symptoms & Treatment for Impetigo
© STDConcern.com
When you have children, it is a good idea to become educated about varying skin conditions that they might develop at different ages. One such infection, called impetigo, tends to affect babies and children under age 6.
According to the Kids Health website, it is caused by two bacteria: streptococcus and staphylococcus aureus. Although impetigo is quite contagious, it is seldom serious. This infection affects mainly children but can effect adults especially in senior citizens homes living close together.
Impetigo Cause
The bacteria that cause impetigo can take up residence on healthy skin. However, it usually finds its way into skin that has been traumatized in some way: through cuts or abrasions, irritation from soaps or hygiene products, or various skin problems.
Symptoms
Mayo Clinic reports that there are several different strains of impetigo, with the most common one being impetigo contagiosa. Also known as non-boullous impetigo, it is caused by strep and staph bacteria. It often appears on the face beside the mouth or nose. Impetigo begins with a red rash that eventually morphs into a brownish scab.
Testing
STD Tests
STD Testing at-Lab (Near Me)
STD Tests at-Home (Kits)
Fertility Tests
Women's Fertility Test at-Home
Health Tests
See All >>
Impetigo Treatment
Interestingly, MedlinePlus states that impetigo often materializes after children recuperate from a respiratory infection. Although impetigo tends to heal up and go away in a few weeks, if a doctor’s care is sought, he will typically prescribe antibiotics to clear it up.
Impetigo is Contagious
When a child with impetigo contagiosa scratches the sores, she can spread the infection to other parts of her body, or even to other people. And children will scratch the impetigo, because it is uncomfortably itchy. Upon healing, impetigo contagiosa leaves a light red scarring on the skin that disappears eventually.
In bullous impetigo, itchy sores form on the skin, as in other types of impetigo. Caused by staph infection, this type of lesion does not hurt as much as other impetigos. Bullous impetigo tends to develop on the torso or appendages of a child younger than 2 years.
The blisters can be a variety of sizes and penetrate into deeper layers of skin than impetigo contagiosa. The lesions eventually develop a yellow crust. Bullous impetigo sores last longer than the other types.
Ecthyma
Another type of impetigo is ecthyma may also plague children. It is different from impetigo contagiosa in a number of ways:
- Its bacteria go deeper into the skin’s dermis layer.
- As the sores form into blisters, they develop a yellowish color.
- The infected child might even have swollen lymph nodes during a bout with ecthyma.
- Upon healing, ecthyma leaves permanent scars.
It is also possible to get the infection through exposure to items touched by the child with impetigo. It is not unusual for several students in a school classroom or nursery school to be stricken with impetigo, due to its ease of transfer on toys, towels, or other shared items.
Conclusion
Although adults can develop impetigo, this is a skin condition chiefly found in children. Preventing transmittal of the infection to others is the biggest challenge when a child is plagued by the condition. So, if you think your child may have impetigo, it may be best to get it checked out by your pediatrician.
Resources
- Kids Health Website
- MedlinePlus
- Mayo Clinic
Products
Life Extension Immune Senescence Protection Formula™ (60 Tablets)
LE’s Best in Class Immune Senescence Protection Formula provides immune system support to rejuvenate the immune system & promote healthy response.
Order Now >>
 Disclaimer: Articles not intended to Diagnose, Treat, Cure or Prevent Diseases.
Disclaimer: Articles not intended to Diagnose, Treat, Cure or Prevent Diseases.
Infections | Education | Products | Testing


